sacral torsion test|what causes sacral torsion : factories Purpose of Test: To assess for sacral torsion. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The examiner palpates the sacral sulcus and inferior angle of the sacrum on each side, while the . webJessica Patez photos & videos. EroMe is the best place to share your erotic pics and porn videos. Every day, thousands of people use EroMe to enjoy free photos and videos. . j ssica cavala jessica alves jessica larissa jessica costa jessica duarte jessica teixeira j ssica jessica marques jessica fit jessica pacheco transando jessica maira .
{plog:ftitle_list}
1 dia atrás · Displaying page 1 of 4974. new. Updated: 2024-02-29
How to identify and treat sacral torsion, sacral shear, and related mechanical chronic low back pain and buttock pain.
If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a posterior sacral torsion. Sacral shears encompass bilateral and unilateral flexion and extension dysfunctions of the sacrum.Purpose of Test: To assess for sacral torsion. Test Position: Prone. Performing the Test: The examiner palpates the sacral sulcus and inferior angle of the sacrum on each side, while the .
Spring Test 1. Find sacral base 2. Place heel of hand over Lumbosacral junction 3. Spring in an Anterior motion 4. Results: a. Positive test = If there is NO springing allowed = Non-neutral .
The Sacroiliac Joint Special Test Cluster, also known as the Cluster of Laslett, is a diagnostic tool used in the assessment of sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain. This test battery consists of 4 (or 5) tests designed to diagnose nociception in the .The sacral thrust test is a pain provocation test used to diagnose sacroiliac dysfunction. One single positive test does not have high diagnostic accuracy but a combination with other sacroiliac pain provocation tests gives valid evidence . The common tests include determination of posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) level in a standing or sitting position, the Gillet test (also known as the march or stork test), the .
Using an SI joint compression technique and/or a Grade 4 or 5 inferior mobilization to the side with the painful SI joint immediately relieved the pain of 12 patients. Whelton has successfully treated more than 1,000 patients .While attempting to rule out other causes of low back pain, provocation tests such as FABRE, distraction, thigh thrust, sacral compression, Gaenslen’s, and sacral thrust can be a useful . Sacral motion described in relation to the L5 vertebra. Sacral torsion or sacral rotation on an oblique axis; Sacral shears (unilateral sacral flexion or extension) Bilateral sacral flexion or extension; Sacral motion .
Sacroiliac joint pain commonly occurs because of anatomic disruption within the joint. Sacroiliac jo . Restricted range of motion in the SIJ causing a torsion, flexion, extension motion pattern. . Upon examination, there is a negative straight leg raise test, but positive thigh thrust, sacral distraction, and sacral compression tests and .The seated flexion test is used to detect sacroiliac joint (SIJ) dysfunction. SIJ dysfunction can be a source of pain in the lower back and buttocks.[1] Toggle navigation. p Physiopedia; p Physiopedia . The test is negative if the movement of the PSISs was symmetrical or positive if one side moved more than the other in the cephalic and/or .Once I started using the stork test again, I realized how many sacral fixations I was missing, and that my previous corrections didn't always correct the fixation. I am once again using this model daily. Top: Position for correction of left anterior sacral torsion; Bottom: Position for correction of left posterior sacral torsion. Sacroiliac (SI) joint injury is a common cause of low back pain. Posterior pelvic joint pain a common name for SI joint dysfunction. The spine and pelvis are connected by the sacroiliac joint. The SI joint lies between the iliac's articular surface and the sacral auricular surface. When an injury occurs to the SI joint, patients often experience significant pain in their .
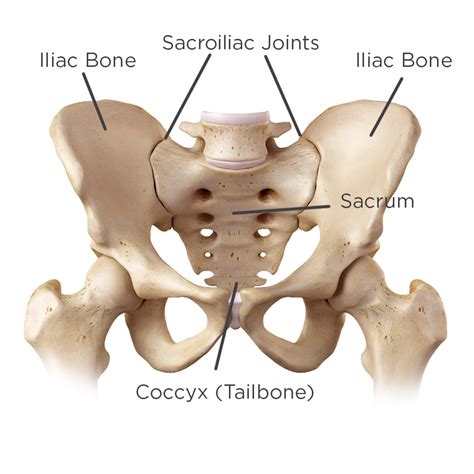
Gaenslen's Test (Gaenslen's maneuver) is one of the five provocation tests that can be used to detect musculoskeletal abnormalities and primary-chronic inflammation of the lumbar vertebrae and Sacroiliac joint (SIJ). The subsequent tests include; the Distraction Test, Thigh Thrust Test, Compression Test and the Sacral Thrust Test.The sacroiliac joints are located on each side of the spine between the two pelvic bones, which attach to the sacrum. The main function within the pelvic girdle is to provide shock absorption for the spine and to transmit forces between the upper body and the lower limbs. The SI joint experiences forces of shearing, torsion, rotation, and tension. Ambulation is heavily impacted .
what causes sacral torsion
Thomas test – one hip flexed to flatten the lumbar spine, other leg relaxed to table. • Normal: hip flexion = 0 degrees, no hip ABD/ADD, and knee flexion = 75 degrees. . (i.e. anterior vs. posteriorly rotated ilium, right vs. left sacral torsion, etc.) that is often taught in most SIJ courses. However, since the individual tests .P a g e | 2 Hesch Institute March 2012 www.Heschinstitute.org Email: [email protected] ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to thank our Creator, my parents Reuben and Bernadine Hesch (both deceased) for Dr. Whelton is a physical therapist who developed several breakthrough treatment methods for immediate pain relief. He has made numerous orthopedic discoveri. Chapter 2 Common presentations and diagnostic techniques Chapter Contents The sacroiliac joint Anatomy, development and aging SI joint mobility Axes of motion Biomechanics Trunk flexion Trunk extension Landing on one leg Vertical forces on the sacrum Ambulation Kinetic function and stability Panjabi: active, passive and neural control systems .
helmet impact testing equipment
Purpose: To assess the contribution of the sacroiliac joint to an apparent leg length discrepancy. Test Position: Supine. . "Four clinical tests of sacroiliac joint dysfunction: the association of test results with innominate torsion among patients with and without back pain." Phys Ther. 1999 Nov;79(11):1043-57. . 08/19/2012. Home: FABER / Patrick’s test; Thigh thrust / femoral shear test; ASIS distraction (supine) Sacral compression (sidelying) Laslett et al report that the accuracy of detecting SI joint dysfunction is increased with at least 3 of the 5 tests are positive. Furthermore, if all 5 tests are negative, you can likely look at structures other that the SI joint.
A look into the evaluation and treatment of sacral torsion's using an Osteopathic approach with muscle energy techniques.
helmet impact testing equipment factory
sacroiliac joint picture diagram
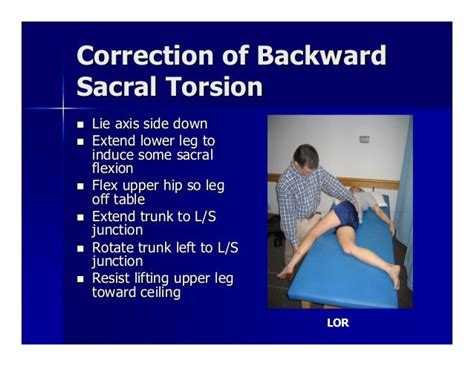
Lumbar / sacral nerve involvement: The nerves of the lumbar and sacral plexus normally are able to slide in and out of the IVF and sacral foramina with the movements of the lower extremity. 3 When they don't, the sacrum and coccyx . 4. THE SACRUM The sacrum, is a large triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of sacral vertebrae S1–S5 , between 18 and 30 years of age. The sacrum is situated at the upper, back part of the pelvic .Sphinx position involves having the patient lie prone, then prop themselves up on their elbows to extend the lumbar spine and flex the sacrum (Figure 1).This can be very uncomfortable for extended or backward torsion sacral dysfunctions. .
Sacral plexus: derives from L4-S4 nerve roots; sits on the internal surface of the piriformis muscle; most of the sacral nerves stemming from the sacral plexus exit through the greater trochanteric notch; the sciatic nerve forms out of sacral plexus and may be compressed by muscle, causing radicular pain down the leg; Coccygeal plexus
Left on Right Posterior Sacral Torsion -- L5 NonAdaptive (FRSright) Non-neutral dysfunctions at L5 (FRSright) often accompany a left on right sacral torsion.An FRSright at L5 can be identified when the patient is backward bent and L5 appears rotated right when compared to a left rotated and right sidebent sacrum.. In the neutral position, when the sacrum is side bent right and .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Upon examining the posterior landmarks of a patient's pelvis, you find the following: deep left sacral sulcus, left inferior/posterior ILA, right positive seated flexion test. Your diagnosis is? a. Left on right sacral torsion b. Left unilateral sacral extension c. Right unilateral sacral extension d. Right on left sacral torsion . After watching this video you will be able to:1. Describe Symmetrical vs Asymmetrical Sacroiliac Joint Movement2. Describe Nutation as the movement of the Sa.
Sacral thrust test; Laslett et al (2005) state that no further examination is wishful if both distraction and thigh thrust test provokes familiar pain because of their high individual sensitivity and specificity. If only one test or 2 other tests are positive, further testing is .
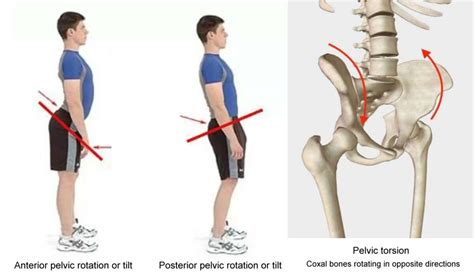
The data do not support the value of these tests in identifying innominate torsion, although the use of these tests for identifying other phenomena (eg, sacroiliac joint hypomobility) cannot be ruled out. Further exploration of the association of Gillet test . Pelvic torsion is known to associate with either the left or right innominate bones (ilia) (see the diagram below) that rotate in an opposite direction around a horizontal axis. This axis runs through a landmark called the symphysis pubis shown by Pitkin and Pheasant in 19362. . manipulating the sacroiliac joint (the client may hear a click .
Brandon Masi Parker shows the diagnosis of the sacrum for torsions and goes over a few of the special tests for the sacrum.The evidence on the amount and direction of sacroiliac motions in a variety of test positions is largely contradictory. Conclusions This review of the literature demonstrates that there tends to be, although certainly not invariably, posterior innominate rotation on the side of .The standing flexion test is a test that can be used to assess sacroiliac joint dysfunction. It is best used in combination with other specific tests. A synonym is the Vorlauf test. Clinically relevant anatomy [edit | edit source] This test involves the sacroiliac joint (SIJ).
sacral torsion treatment
People Playground is a physics-based simulation game that unleashes your creativity in .
sacral torsion test|what causes sacral torsion